If you’re like most people, you’ve probably stood shirtless in front of a mirror, pinched your belly, and turned side to side to check if what you’re holding onto is fat or loose skin. You’ve probably also used a fat caliper to confirm your findings.
Body fat or loose skin is also a major concern for lifters trying to build a shredded six-pack. Both these conditions can hinder your plans of dressing up as Dwayne “The Rock” Johnson in Baywatch (2017) on Halloween.
Loose skin and fat occur for various reasons and should be easy to spot if you know what you’re looking for. Losing fat too quickly is one of the main reasons behind saggy skin, whereas an unbalanced diet and a sedentary lifestyle cause fat accumulation.
In this article, we dive into how to differentiate between loose skin and fat, their causes, and how to avoid and fix these areas of concern.
What is Loose Skin?
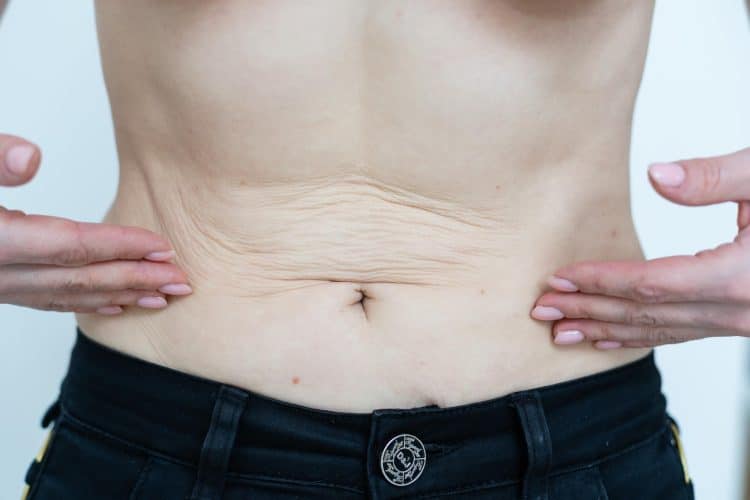
Loose skin, also known as sagging skin, occurs when your skin loses its natural elasticity and looks loose, sagging, or wrinkled. Saggy skin is most commonly seen in the arms, thighs, abdomen, and face.
Wrinkles and folds and a loss of firmness are the most common characteristics of sagging skin. All these effects primarily occur in areas with significant weight loss or skin damage. Saggy skin has a thin texture and can feel paper-like to the touch. It happens because of a loss of elastin and collagen.
During quick weight loss, it is hard for the collagen and elastin fibers to return to their original state as the fibers shrink and contract too quickly. As you age, it becomes more difficult for your skin to contract and bounce back. [1]
Common Causes of Loose Skin
These are the most common causes of sagging skin:
Weight loss
Rapid and significant weight loss are the most common reasons behind the formation of loose skin. When you lose weight too quickly, your skin might not be able to contract and tighten in time according to your new, smaller structure, causing loose skin.
Aging
Our skin loses elasticity and firmness as we age. Most elderly people have loose skin. The sagging skin issue might compound if older folks lose fat or muscle mass due to hormonal changes. Sun damage, smoking, or other poor lifestyle choices can also exaggerate skin sagging.
Pregnancy
A woman’s body undergoes significant changes during pregnancy, including hormonal changes, weight gain, and skin stretching. Many women experience sagging skin in their abdomen, thighs, and breasts after giving birth, as their skin cannot return to its original form fast enough.
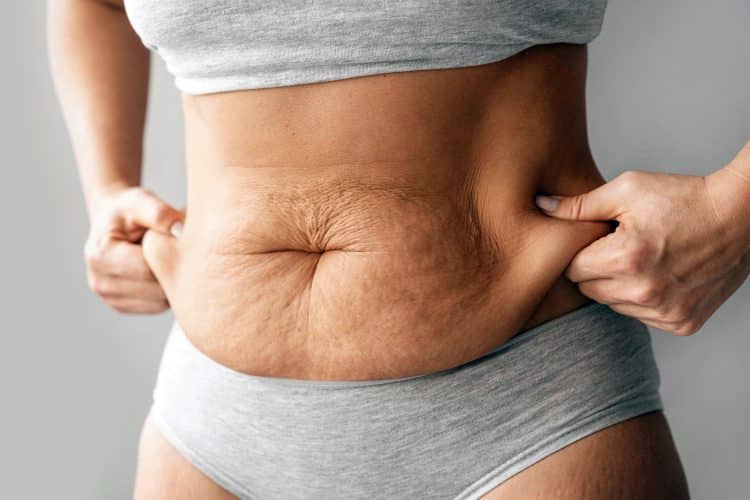
Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role in your skin elasticity. Some folks are more prone to develop stretch marks due to naturally less elastic skin. It can also result in sagging skin if the individual undergoes rapid weight loss.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome can hamper your body’s ability to produce collagen and elastin, increasing your risk of sagging skin.
How to Prevent Loose Skin From Forming
You could lower your risk of developing loose skin by following these tips:
- Planned Weight Loss: Rapid weight loss is one of the most common reasons behind the formation of sagging skin. Follow a planned weight loss regimen to limit this risk. Limit your weight cut to 1-2 pounds per week.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights helps build muscle and can improve the underlying structure of your skin.
- Healthy Diet: You must switch to a macronutrient-focused balanced diet to meet your daily nutrient goals.
- Wear Sunscreen: You should never step out without sunscreen as it can prevent premature aging and skin sagging and improve skin elasticity.
- Cut Out Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are notorious for damaging skin and hampering skin elasticity.
- Hydration: Drinking at least a gallon of water daily can improve your skin’s elasticity and lower your risk of developing sagging skin.
Treatment Options for Loose Skin
Here are the ways to treat loose skin:
- Exercise: Doing 3-5 weekly HIIT workout sessions can help burn excess fat and eliminate loose skin. Do at least 20 minutes of daily cardio.
- Foods and Supplements: Vitamin C, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, copper, zinc, iron, and selenium, and collagen supplements can help improve skin elasticity and fix sagging skin.
- Topical Treatments: Compounds such as retinol can help boost collagen production in the skin and make your skin more supple.
- Non-Surgical Options: Radiofrequency, ultrasound, and laser therapy are a few non-surgical treatments for fixing loose skin.
- Surgical Options: Tummy tuck, thigh lift, or arm lift are a few popular contouring procedures for treating sagging skin.
Read also: Most Important Supplements for Men Who Lift
What is Fat?
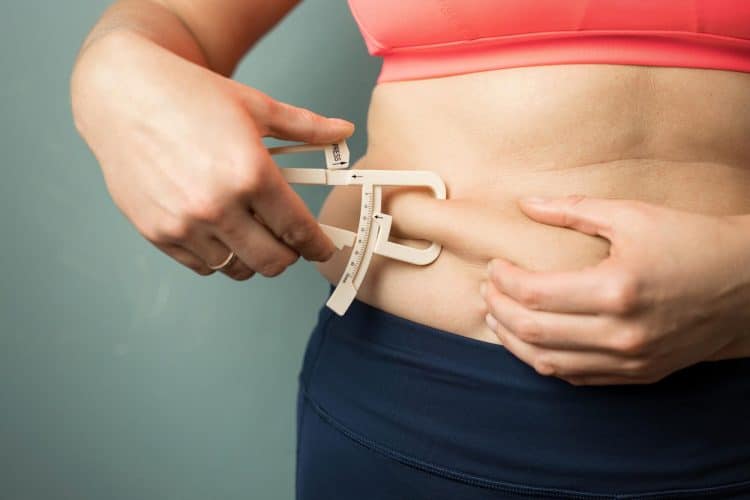

Fat, also known as adipose tissue, is present throughout the body. It is a connective tissue that insulates and protects our organs. Our body stores energy in the form of fat, which it uses after it has burned through its glycogen reserves. There are two types of fat — subcutaneous and visceral.
Types of Fat
Subcutaneous fat is located just beneath the skin. It is visible and popularly associated with body weight. Subcutaneous fat provides insulation and protection to the body and acts as an energy reserve.
Visceral fat is present deep inside the body and surrounds the organs in the abdominal cavity. It is also known as organ fat. Although not visible, visceral fat is more metabolically active and associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Subcutaneous fat is typically softer and easier to move, whereas visceral fat is more dense and difficult to move.
Common Causes of Fat Accumulation
There are several causes of fat accumulation in the body, including:
Poor Diet
An unbalanced diet and poor lifestyle choices are the most common reasons for fat accumulation. A diet rich in calories, saturated and trans fats, and added sugars increases your odds of storing excess fat.

Lack of Exercise
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to a prolonged calorie surplus, resulting in excess fat stores in the body. Staying active throughout the day aids in burning calories, which can help maintain a healthy weight.
Genetics
Like in the case of loose skin, genetics can play a crucial role in fat distribution and your tendency to accumulate fat in certain areas.
Stress
Chronic stress can spike your cortisol levels, making you hold water and store excess fat. It is most prominent in the abdominal area.
Hormonal Balance
Hormonal imbalances during certain live phases can contribute to fat accumulation in the body. People going through puberty, menopause, pregnancy, or certain medical conditions might experience a sudden fat buildup.
How to Reduce Fat Through Diet and Exercise
Here is how to reduce body fat through nutrition and training:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: It is your most potent weapon to reduce body fat. Eat a macro-balanced diet that focuses on protein. Protein can help you feel fuller for longer and aid in building muscle.
- Enter a Caloric Deficit: This is the holy grail of losing weight. You must burn more calories in a day than you consume to lose weight. It will push your body to burn your fat stores for energy.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed and high-fat foods lack nutrients and are packed with calories. Focus on consuming whole, nutrient-dense foods during your weight loss journey.
- Supplements: Using a fat burner and whey protein isolate supplement can help you in your weight loss journey.
- Increase Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle does not help in burning calories. You must do at least one 20-minute LISS cardio session daily to supercharge your weight loss progress.
- Engage in Strength Training: Besides building muscle mass, strength training can help boost your metabolic rate. A high metabolic rate ensures you burn fat throughout the day, even when you are not physically active.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking a gallon of water daily ensures that you don’t overeat and helps keep you satiated.
Medical Treatments for Fat Reduction
Folks that are having trouble losing fat through the diet and training tips mentioned above can opt for the following medical treatments after consulting a qualified healthcare expert:
- Surgical Procedures: Liposuction is the most popular surgical procedure for fat reduction. It involves fat removal from specific body areas through a small incision. This procedure is typically done on the abdomen, hips, thighs, and buttocks.
- Non-Invasive Procedures: Cryolipolysis (cool sculpting), laser lipolysis, and radiofrequency lipolysis are some of the non-surgical fat loss procedures.
Differences Between Loose Skin and Fat
Given below are a few physical characteristics and differences between saggy skin and body fat:
- Texture: Loose skin is usually thin and wrinkled, whereas body fat is smooth and firm. Saggy skin is easier to pinch and pull than body fat.
- Appearance: Loose skin is saggy or droopy, especially in areas where you have experienced significant weight loss. Loose skin leads to wrinkly skin and can create folds. On the other hand, excess body fat gives your body a rounder shape.
- Firmness: Loose skin feels soft and paper-like to the touch. On the flip side, body fat is firmer and more resistant to pressure.
How To Differentiate Between Loose Skin and Fat
Here are six ways to differentiate between loose skin and fat:
Texture and Appearance
As mentioned earlier, one of the most prominent differences between loose skin and fat is that saggy skin can be pinched and pulled out easily. In contrast, it is difficult to pinch and pull on body fat. Hence, performing a pinch test is a reliable method of ascertaining if you’re dealing with loose skin or fat. Furthermore, loose skin is thin and wrinkled, whereas body fat is smoother and firmer.
Location
Most people overlook the location of the concerned area while differentiating between loose skin and fat. However, it can be crucial in differentiating between excess body fat and saggy skin.
Loose skin is often seen in arms, thighs, and abdomen as these areas experience the most significant weight loss. During a weight loss program, you’ll first notice the changes in your upper arms, legs, and midriff, making them the most prone to loose skin. On the other hand, fat can be found all over your body.
Weight Loss History
Folks that lose significant weight quickly have higher chances of developing saggy skin. Conversely, people who have recently gained weight are likely to experience loose skin. [2]
Use a Pinch Test
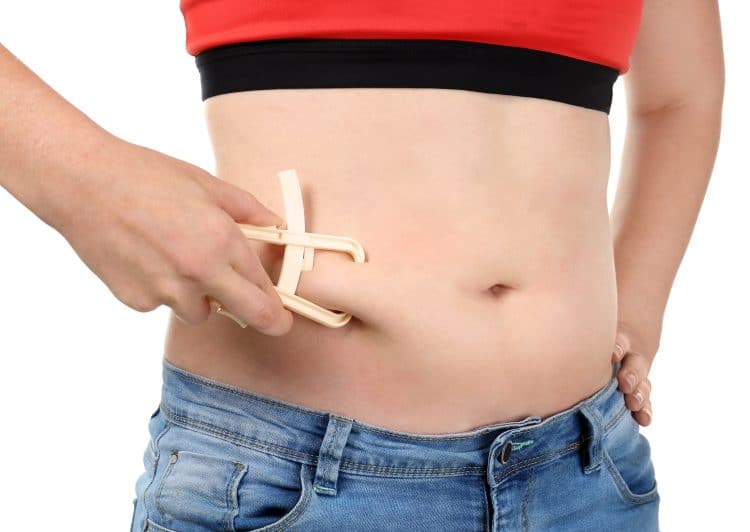

Although the pinch test is not as accurate as a caliper test, it is enough to differentiate between loose skin and fat. There are two ways of conducting the pinch test.
This is how to perform the first pinch test:
- Use your thumb and index finger to perform the pinch test.
- Grab the fat of the concerned area between your fingers and give it a few rolls. If the skin feels stretchy and sloppy, it’s loose skin. Conversely, if the skin feels thick and dense, it’s body fat.
The second method requires adhering to the following steps:
- Pinch the skin between your thumb and forefinger.
- Pull the skin away from your body.
- If you can pull the skin 1-inch or more away from your body, it is loose skin. Furthermore, you’ll feel your thumb and forefinger touch while pulling away the skin.
- On the other hand, you shouldn’t be able to pull fat an inch away from your body. During this step, you’ll have a thick chunk of fat between your fingers.
Take the Bounce Test
If unsatisfied with the pinch test, you should try the bounce test. The bounce test is much easier (and fun?) than the pinch test, which might sting if you go too hard on it.
To perform the bounce test, place your fingers under the concerned area and give it a light bounce. If the area feels elastic and bouncy, you’re dealing with loose skin. On the other hand, it is body fat if it resists bouncing and feels solid.
Undergo a Professional Caliper Test
The keyword here is ‘professional.’ Folks that take the caliper test at home or in the gym often follow incorrect parameters to skew the results in their favor. Caliper tests performed by doctors and trained medical professionals will give precise details about your body fat.
Medical professionals use calipers to measure the skin folds in specific locations and give you your exact body fat percentage. They’ll also help you determine if you’re dealing with body fat or loose skin.
Notably, differentiating between loose skin and fat is easier said than done. Loose skin and excess fat can often occur together, especially in areas where you experience significant weight loss. Conversely, the elderly can develop saggy skin and gain body weight because of hormonal changes. Telling loose skin from body fat will not always be clear-cut. You must weigh all the factors before embarking on the solutions.
[sc name=”style-summary2″ ]
Related:
[/sc]
Importance of Understanding The Differences Between Loose Skin and Fat

Knowing the differences between saggy skin and body fat is vital for the following reasons:
Treatment
Many people make the mistake of putting loose skin and body fat on the same scale, which worsens their condition in the long run. Understanding the difference between the two can help you choose the correct treatment option, streamlining your progress.
Health Risks
Excessive body fat comes with several health issues like increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, etc. On the other hand, loose skin mostly results from losing weight too quickly, aging, or pregnancy, which doesn’t pose health risks.
Knowing the difference between loose skin and body fat can help you preempt the negative effects of these conditions, reducing the risk of developing these conditions in the future.
Weight Loss Goals
The ability to differentiate between body fat and saggy skin will put you on the fast track to achieving your weight loss objectives. It will also help you track your progress more accurately. Furthermore, it saves you from mistakes like starting a weight loss program for your loose skin caused by aging.
Self-Esteem
Thanks to the aesthetics-driven world we live in, loose skin or body fat can cause serious self-image issues. Understanding the difference between the two can help you pick the right treatment path, which can help improve your body image.
Wrapping Up
Contrary to what many people think, loose skin and fat accumulation can happen at the same time and site. It can make it difficult to differentiate between the two. However, correctly analyzing your area of concern is critical to choosing the right treatment option.
Checking the concerned area’s texture, shape, location, and firmness, analyzing your weight loss progress, and conducting the pinch, bounce, and caliper tests can help you determine if loose skin, fat, or both are contributing to your troubles. If you have any questions about loose skin or body fat, drop them down in the comments below, and we’ll be happy to help!
References
- Uitto J, Li Q, Urban Z. The complexity of elastic fiber biogenesis in the skin–a perspective to the clinical heterogeneity of cutis laxa. Exp Dermatol. 2013 Feb;22(2):88-92. doi: 10.1111/exd.12025. Epub 2012 Oct 23. PMID: 23088642; PMCID: PMC3556375.
- Sami K, Elshahat A, Moussa M, Abbas A, Mahmoud A. Image analyzer study of the skin in patients with morbid obesity and massive weight loss. Eplasty. 2015 Jan 23;15:e4. PMID: 25671051; PMCID: PMC4311578.



I still need help differentiating!! The area I’m talking about is my face – my cheeks. My cheeks are quite soft and easy to pinch, however there are no wrinkles surrounding it. Additionally, it’s very round and whenever I turn my head down/look down, it droops. I’ve been confused if I have fat or saggy skin. Send help!
Hi Amelia,
You have a very specific question; however, the details you’ve provided are not enough. Several factors, including age, genetics, family history, and other health conditions, can influence fat build-up or loose skin. Plus, your overall body fat percentage also needs to be considered. It is extremely hard to do this analysis over text. I recommend consulting a healthcare professional to confirm whether it is fat or loose skin.