Do you struggle with weight loss or shed a few pounds only to see them come back in a short period? Have you tried all types of diets under the sun but have little to nothing to show for it?
On the other hand, you might see people eating a boatload of carbs and still maintaining a healthy body weight, making you feel like you have a metabolism problem.
But is your metabolism a problem, or is it more efficient with specific foods?
The second scenario is based on the theory that everyone is unique, and your body oxidizes certain nutrients more efficiently than others.
Let’s understand more about different metabolic types with a focus on fat protein efficiency and foods that can help you lose or maintain weight if you belong to this metabolic type.
Related: Anabolic Vs. Catabolic Metabolism – Definitions and How They Affect You
Metabolic Typing Diet: What We Know
The metabolic typing diet is based on the theory that eating according to your metabolic needs reduces food cravings, boosts energy, and helps you reach your ideal weight.
One of metabolism’s purposes is to burn food for energy. It is unique for each individual and depends on their genetics and environmental factors.
According to this diet, your metabolism depends on the following two factors: (1)
Cellular oxidation
Cellular oxidation is how fast your body converts food into energy.
The most dominant autonomic nervous system
The autonomic system consists of two parts — the energy-conserving parasympathetic nervous system and the energy-burning sympathetic nervous system.
These factors determine your metabolic type and the types of food you should eat.
Check Out: 6 Ways To Boost Your Metabolism And Lose Fat
Three Metabolic Types
Considering the mentioned factors, you may be classified as a slow, fast, or normal oxidizer.
In slow oxidizers, the sympathetic nervous system dominates. On the other hand, the parasympathetic system dominates in fast oxidizers. A normal oxidizer has a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
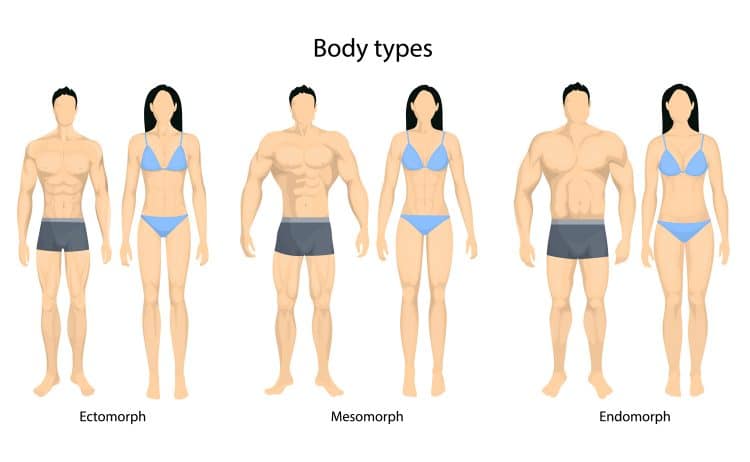
So, your diet plan should be based on the category you belong to: (2)
Fat Protein Efficient (Fast Oxidizer/Ectomorph)
People in the fat protein efficient group burn food to get energy quickly. Such individuals are usually highly active with a very physical job.
As their body efficiently burns food for energy quickly, they might have to eat in short intervals. People with this type may crave sweet or salty, feel tired, and experience anxiety while eating a high-carb diet.
These individuals may benefit from a more fat protein efficient diet plan than a carbohydrate efficient one.
Carbohydrate Efficient (Slow Oxidizer/Endomorph)
People with this type of metabolism break down food slowly. These individuals usually lead a sedentary lifestyle and don’t need much energy.
Their body tends to store excess nutrients that they don’t use. These individuals thus don’t experience hunger often. On a high protein diet, they may be tired, overweight, and experience indigestion.
These individuals may benefit from more complex carbohydrates than a fat protein efficient diet plan.
Mixed (Mixed Oxidizer/Mesomorph)
People with mixed metabolism types have normal digestion. The rate at which the body burns food is neither too fast nor too slow.
They usually have a hearty appetite and need a stable mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Must Read: Body Type Quiz: Find Your Body Type Endomorph, Ectomorph, or Mesomorph?
More on Fat Protein Efficient Metabolism
Now you know that fat protein efficient individuals are fast oxidizers and have a dominant parasympathetic system. They burn food quickly and have a large appetite.
They usually feel hungry on a high-carbohydrate diet and crave sweet, salty, and fatty foods.
If you belong to this type, you should get 50% of calories from protein, 20% from fat, and 30% from carbohydrates. Doing so will allow you to optimize your metabolic process and lose excess weight. (3)
How To Know If You’re Fat Protein Efficient?
Unfortunately, there’s no test to figure out your metabolic type. Experts suggest carrying out some blood and urine tests to understand your metabolism.
Some signs that may suggest you’re fat protein efficient include:
- A big appetite
- Feeling hungry often
- Craving salty more than sweet
- Feeling grumpy and tired after high-carb meals
- Feeling full and energized after high-protein meals
Should You Try A Fat Protein Efficient Diet?
If you’re a fast oxidizer, it makes sense to try a fat protein efficient diet. This is because the body breaks down carbohydrates as the first energy source. So as soon as you consume carbohydrates, they are metabolized to provide instant energy. However, you might feel hungry after a short while.
Consuming more proteins and fats will result in the slower digestion of food. Usually, protein and fats take longer to metabolize than carbs, eliminating excessive hunger that might lead to overeating.
The best part of knowing your metabolic type is that you can tailor your existing diet according to your needs.
For instance, following a keto diet may help if you’re fat protein efficient. Framing your diet around your metabolic type involves eating a healthy diet and doesn’t involve restrictions in typical diets.
A fat protein efficient diet involves adjusting your macronutrients around healthy foods (more on this below).
All in all, there’s no harm in trying this diet as it focuses on an individualized and healthy approach to nutrition.
Is Fat Protein Efficient Diet Same as Keto Diet?
The simple answer to the question is no.
While both diets prioritize fat and protein consumption over carbohydrates, they aren’t the same.
The keto diet focuses on a high fat, protein diet regardless of your metabolic type.
Individuals with fat protein efficient metabolism might find keto beneficial for weight loss. However, the typical keto diet advises you to get only five percent of calories from carbs in contrast to 30 percent carbs in a fat protein efficient diet. (4)
Moreover, a keto diet may leave you foggy, constipated, irritable, or nauseous due to the low carb intake. These side effects are usually referred to as the keto flu and are associated with carbohydrate withdrawal.
These side effects aren’t observed with a fat protein efficient diet as you still get 30 percent of calories from carbs.
Check Out: What is Keto Diet? Benefits, Drawbacks, and Sample Meal Plan
What To Eat on A Fat Protein Efficient Diet?
The primary aim of this diet is to consume meals rich in protein and fats. The breakdown of the energy coming from different macronutrients is:
- 50% from protein
- 20% from fats
- 30% from carbohydrates

Protein-rich foods include:
- Nutrient-dense meats such as organ meats, beef, and dark meat chicken
- Fatty fish such as salmon and tuna
- Tofu
- Buckwheat
- Quinoa
Related: Foods that contains highest protein
Healthy fat sources are:
- Eggs
- Avocado
- Full-fat dairy
- Oils
- Seeds and nuts
Healthy sources of carbohydrates are:
- Asparagus
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
Some ideas for a fat protein efficient diet plan:
Breakfast
- Greek yogurt with blueberries
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Steamed salmon with cream cheese
Lunch
- Tuna with broccoli
- Chicken thighs with leafy greens
- Leafy green salad with feta cheese
- Broiled salmon with leafy greens
Dinner
- Steak with a bit of quinoa
- Broiled chicken with asparagus
- Bread-free vegan hamburger
- Roasted fish with a small serving of brown rice
Related: Protein Calculator: Find Your Daily Protein Intake
What are the Benefits of a Metabolic Typing Diet?
Every individual has a unique metabolism and dominant autonomic system. The primary benefit of this diet is understanding the types of food that suit your body and the proportion in which you need to consume them.
Some benefits of the diet include:
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Getting rid of extra pounds
- Reducing food cravings
- Reducing mood fluctuations
- Having enough energy throughout the day
Lastly, the diet encourages limiting processed foods such as sugar and white rice that spike your blood sugar levels.
Downsides To Eating For Your Metabolic Type
There may be downsides to eating according to your metabolic type if it prevents you from getting the minimum recommended nutrients. It may also lead to nutritional deficiencies if you follow it long-term.
Besides, a high protein and fat diet may increase cholesterol levels and the risk of heart diseases if it’s rich in saturated fats. (5)
As the diet is rich in purines, it may increase the build of uric acid in the body, increasing the risk of gout and kidney diseases. (6)
FAQs
What should you eat if you are fat protein efficient?
You can eat foods rich in healthy fats and protein. Some examples include:
- Dark meat chicken and red meat
- Organ meats such as beef liver
- Fatty fish such as tuna, salmon, mackerel
- Lean pork loin
- Full-fat dairy such as butter, eggs, yogurt, cheese, and cream
- Low-sugar fruits such as grapefruit, avocado, melon, berries, kiwi, and oranges
What does it mean to be protein and fat efficient?
According to metabolic type theory, people that are protein and fat efficient have a faster metabolism and oxidize their food quickly.
Some signs that you can be protein and fat efficient include feeling hungry in short intervals, a strong appetite, and salt craving.
Is a protein and fat diet good?
In most cases, a high protein and fat diet is not harmful, especially when carried out for a shorter time. Following a diet based on your metabolic type is the key. Such diets can help you feel energetic and support weight loss.
Is this a fad diet?
A fad diet gets popular for a short time without being a standard dietary recommendation and is likely to fade away. So, a fat protein efficient diet can be called a fad diet.
The Takeaway
A metabolic typing diet is a method that focuses on individualized nutrition. Your body is unique and can digest some macros better than others. Understanding your body type can help you feel satiated, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent overeating.
There are no significant downsides to following a fat protein efficient diet if you belong to the category. However, you should focus on nutrient-dense whole food and not restrict any of the macros.
If you feel full and energized between meals, it may be worth trying it for the long term. If you feel grumpy and hungry, you can avoid it.
References
- Harvard Health Publishing. The truth about metabolism.
- WebMD. What Your Body Shape Says About Your Health.
- Clarke D, Edgar D, Higgins S, and Braakhuis A. Physiological analysis of the metabolic typing diet in professional rugby union players.
- Batch, J. T., Lamsal, S. P., Adkins, M., Sultan, S., & Ramirez, M. N. (2020). Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet: A Review Article. Cureus, 12(8), e9639.
- MedlinePlus. Facts about saturated fats.
- NIH. Purines.


