Barbell back squats are often called the king of exercises. Entire workouts have been built around the back squat, including the classic old-school 20-rep squat routine. It’s safe to say that the squat is a VERY productive exercise for building muscle mass and strength.
All of that said, there are drawbacks to squats. For starters, you need a squat or power rack to perform heavy squats safely. Getting pinned under a heavy bar can cause severe injury. Barbell squats also require a high degree of technical proficiency to perform safely. An ugly squat is often a dangerous squat.
And then there is the whole “squats are functional” thing. While squatting (the movement) is highly functional, when was the last time you did a squat with a heavy weight on your back outside of the gym? Probably never, right?
All this means that the barbell deadlift could be the real king of exercises. You don’t need a rack to do them, and they teach you how to lift heavy weights off the floor, making them a REAL functional exercise. Plus, if you want to build real-world strength and useable muscle mass, the deadlift delivers.
That’s not to say that squats are bad, but deadlifts may be better.
All squats vs. deadlift arguments aside, there are several different types of deadlifts for you to choose from. In this article, we compare and contrast the partial and full deadlifts so you can decide which is the best one for you.
- What is Partial Deadlift?
- Partial Deadlifts – Pros
- Partial Deadlifts – Cons
- What is Full Deadlift?
- Full Deadlifts – Pros
- Full Deadlifts – Cons
-
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Strength
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Hypertrophy
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Safety
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Ease of learning
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Equipment
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Long-term progression
- Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Variety
- Partial Deadlifts Vs. Full Deadlifts – Wrapping Up
What is Partial Deadlift?
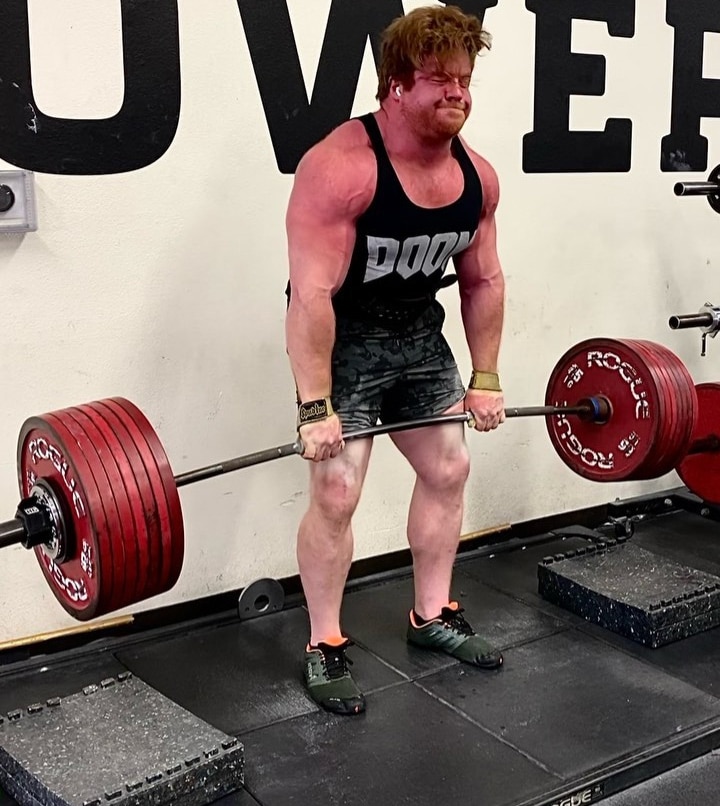

The partial deadlift involves starting your rep with the bar higher off the floor than usual. For full or conventional deadlifts, the standard bar height is nine inches. That’s because standard 45lbs/20kg Olympic bumper plates have a diameter of 18 inches.
With partial deadlifts, you raise the bar by placing it on blocks or in a power rack with the safety bars set at your preferred height. This reduces your range of motion and changes several aspects of the lift. Partial deadlifts are also known as block pulls and rack pulls, named after the equipment used to elevate the bar.
Powerlifters frequently use partial deadlifts as an assistance exercise to increase conventional deadlift performance. They also feature in strongman competitions where deadlifts often start from a higher position, e.g., the silver dollar deadlift. Partial deadlifts also offer benefits to bodybuilders and general exercisers.
Muscles Worked
The partial deadlift is a compound exercise involving multiple muscles and joints working together. From top to bottom, the main muscles tested and trained by partial deadlifts are:
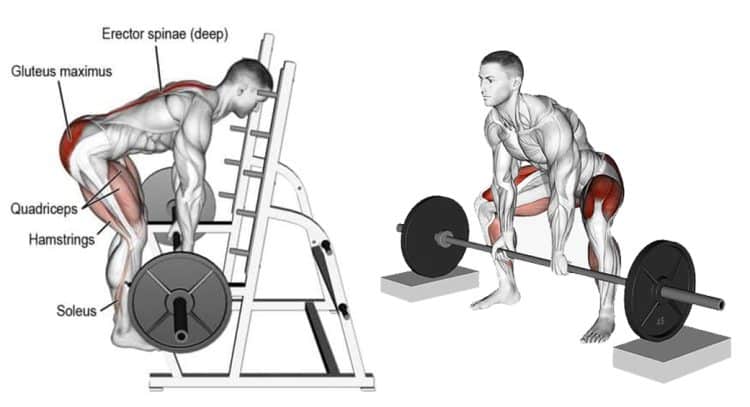
- Trapezius – upper back
- Rhomboids – between the shoulder blades
- Deltoids – shoulders
- Latissimus dorsi – side of the upper back
- Core – muscles of the midsection, including the abs and lower back
- Biceps – front of the upper arm
- Forearm flexors – gripping muscles
- Gluteus maximus – back of the hips
- Hamstrings – back of the thigh
- Quadriceps – front of the thigh
- Triceps surae – calf muscles
Needless to say, partial deadlifts are a very comprehensive exercise that works almost every muscle in your body. Do a few sets of bench presses, dips, or push-ups, and you can theoretically train your entire body with just two exercises.
How To Do Partial Deadlifts
Get the most from partial deadlifts while keeping your risk of injury to the minimum by following these step-by-step instructions!
- Set your barbell in a power rack or on blocks so it’s between lower knee and mid-thigh height. The lower the bar, the more work your glutes and hamstrings have to do.
- Stand close to the bar so it’s touching your legs. Your feet should be between hip to shoulder-width apart.
- Hinge forward from your hips, bend your knees slightly, and grab the bar. Hold it using a shoulder-width double overhand or mixed grip. Flex your lats and upper back.
- Brace your core, straighten your arms, and lift your chest. Take any tension out of the bar.
- Drive your feet into the floor, push your hips forward, and stand up. Do not bend your arms or round your lower back. Take care not to lean back at the top of your rep.
- Lower the bar back down under control, allow it to settle for a second or two, reset your core and grip, and repeat.
[sc name=”style-summary2″ ]
Tips:
- Use gym chalk and/or lifting straps to reinforce your grip.
- Wear shoes with flat soles and low heels for stability.
- Use a weightlifting belt for support and safety.
- This exercise works best with low reps and heavy weights.
- Do not use a deadlift bar for this exercise, as doing so may damage it.
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts – Pros
Not sure if partial deadlifts deserve a place in your workouts? Consider these advantages and benefits and then decide!
Better for tall and inflexible lifters
Bending down to deadlift a weight from the floor requires excellent hamstring flexibility. Tall people may also find bending over so far challenging. Because of this, some lifters end up rounding their lower backs during deadlifts, increasing their risk of injury.
Partial deadlifts start with the barbell raised, making it easier to reach if you are tall or inflexible. This means that partial deadlifts are often more lower back-friendly than deadlifts from the floor.
Lift heavier weights
Partial deadlifts involve a shorter range of motion than full deadlifts. Because of this, you should be able to lift heavier weights compared to conventional deadlifts. Lifting heavier weights will build more strength, especially in your upper back and grip.
Build a bigger back
Bodybuilders use partial deadlifts to increase back size and width. The partial deadlift involves every major upper, lower, and mid-back muscle, and using heavy weights is one of the best ways to increase back thickness and density.
Overcome your sticking points
Like most freeweight exercises, full deadlifts have sticking points. Some lifters struggle to break the bar away from the floor, while others get stuck at the midpoint of their rep and battle to lock out their hips.
Partial deadlifts allow you to work on your lockout, so you are more likely to be able to complete your conventional deadlift reps successfully.
Fatigue management
Full deadlifts are incredibly fatiguing. They challenge your entire body and central nervous system, especially if you do very low reps, e.g., 1-3 per set. Partial deadlifts are a little less taxing as the range of motion is less.
So, if you are feeling too tired to do full deadlifts, you may find that you can still perform partials. Alternatively, you can alternate between full and partial deadlifts if you want to avoid accumulating too much fatigue, e.g., because you deadlift twice a week.
Partial Deadlifts – Cons
While partial deadlifts are an effective exercise, there are a couple of drawbacks to consider, too:
Equipment
You’ll need pulling blocks, a power rack, or stacks of bumper plates to do partial deadlifts. If you cannot raise the bar off the floor, you won’t be able to do this exercise. In contrast, all you need for full deadlifts is a bar and weight plates.
You can lift more weight
While this is a pro, it can also be a con. Just because you can lift more weight doesn’t mean you should! Some lifters load up the partial deadlift and use way more weight than they can handle safely. This can lead to injury, especially to the lower back.
Not as functional
Most strenuous lifting activities start with a weight resting on the floor. Partial deadlifts begin with the weight raised, so you could become “weak off the floor” if you never do full deadlifts.
What is Full Deadlift?
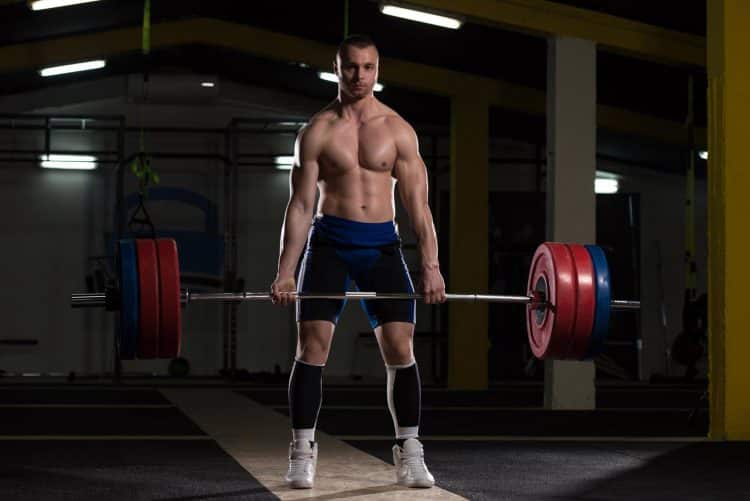

The full or conventional deadlift is so-called because each rep starts with the weight resting on the floor. In other words, it’s a “dead” weight. When talking about deadlifts, most people are referring to full deadlifts rather than partials.
The deadlift is a popular exercise with all strength athletes and is the final lift contested in powerlifting events. Deadlifts also feature in most strongman competitions. Bodybuilders do deadlifts to build upper and lower body strength and muscle size. Even booty girls do deadlifts as it’s such an effective hip and butt-builder.
The current world record for the deadlift is 501kg/1,104.5lbs, held by strongman Hafþór Júlíus Björnsson. However, Eddie Hall’s 500kg lift is the heaviest ever in strongman competition.
Muscles Worked
Full deadlifts work the same muscles as partials. However, full deadlifts involve more lower-body engagement. This is because you must flex your knees and hips more to reach the floor.

The muscles tested and trained during full deadlifts are:
- Trapezius
- Rhomboids
- Deltoids
- Latissimus dorsi
- Core
- Biceps
- Forearm flexors
- Gluteus maximus*
- Hamstrings*
- Quadriceps*
- Triceps surae
*Greater involvement compared to partial deadlifts.
How to do full deadlifts
Get the most from full deadlifts while minimizing the risk of injury by following these guidelines!
- Place your barbell on the floor. Use standard 45lbs/20kg plates or raise the bar on blocks so it’s around nine inches off the floor.
- Stand with your feet between hip and shoulder-width apart, toes under the bar. The bar should lightly touch your shins.
- Lean forward and hold the bar with an overhand or mixed shoulder-width grip.
- Straighten your arms, drop your hips, brace your core, and raise your chest. Pull the slack out of the bar. Flex your lats and press the bar toward your legs.
- Drive your feet into the floor and stand up, pushing your hips forward as you rise. Make sure your hips do not come up faster than your shoulders.
- Stand up straight but avoid leaning back.
- Lower the bar under control back to the floor, allow it to settle, reset your core and grip, and repeat.
Learn more about perfecting your deadlift form here.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Tips:
- If using a mixed grip, switch your hands around set by set to avoid muscle imbalances.
- Deadlift in flat shoes or just your socks to maximize posterior chain engagement.
- Do not allow your lower back to round during deadlifts, as doing so can cause severe injury.
- Use chalk and/or straps to reinforce your grip.
- Wear a weightlifting belt for safety and support.
[/sc]
Full Deadlifts – Pros
Are full deadlifts the best variation for you? Consider these benefits and then decide!
A very functional exercise
Full deadlifts teach you how to safely lift heavy objects from the floor. This is a common feat of strength that many people must perform daily, e.g., lifting kids, pets, grocery bags, etc. Full deadlifts develop functional or useful strength that can help you in the real world outside of the gym.
A total muscle builder and strengthener
Full deadlifts work almost every major muscle in your body – upper and lower. As such, they’re an excellent option for time-pressed exercisers who don’t have time for more convoluted workout plans.
So, whether you want more muscular legs, a broader back, or an unbreakable grip, full deadlifts will give you what you want.
A standardized lift
Providing you use Olympic bumper plates, all full deadlifts should be more or less identical and, therefore, comparable. So, if you lift 220lbs in Boston, you should have no problem repeating your lift in New York.
In contrast, partial deadlifts can start from almost any height, making it much harder to compare your performances. Starting with the bar at 12 inches feels very different to 15 or 18.
Lots of options and variations are available
Partial deadlifts are a variation of full deadlifts, and there are plenty more to choose from. Additional full deadlift variations include:
- Paused deadlifts
- Sumo deadlifts
- Deficit deadlifts
- Banded deadlifts
- Single-leg deadlifts
- Touch ‘n’ go deadlifts
- Hack deadlifts
- Snatch grip deadlifts
All these variations (as well as partial deadlifts) mean your deadlift workouts never need to be repetitive or boring.
Full Deadlifts – Cons
There are also a couple of drawbacks to full deadlifts to consider:
Increased lower back stress
Bending forward to reach a barbell on the floor puts a lot of stress on your lower back. This can be a problem for people suffering from lower back pain. This stress is highest for taller lifters and those with tight hamstrings.
Related: 3 Reasons Your Back Hurts After Performing Deadlifts
A complex exercise
Contrary to what you might think, full deadlifts are quite technical and require skill to perform safely. Common deadlift form faults include rounding the lower back, letting the hips rise faster than the shoulders, “squatting” the bar up, and lifting your heels.
Some lifters, especially beginners, may need help learning the deadlift. Given its potential to cause injury, the deadlift should not be taken lightly!
A very taxing exercise
The full deadlift is so demanding that some lifters only do a few sets a week. In contrast, others only train heavy deadlifts every 10-14 days. A heavy deadlift workout will take a lot out of your body, taxing not only your muscles but your central nervous system.
This could be a problem if you also need energy for other activities, e.g., a sport you’re training for.
Some people hate deadlifts!
Heavy, high-rep deadlifts are tough. It’s not uncommon to feel faint or sick after a set of deadlifts. But, of course, this demand is what makes deadlifts so effective. Still, for those of a less masochistic persuasion, the difficulty of deadlifting means they dread or hate doing deadlifts.
The good news is that deadlifts are NOT compulsory, and there are plenty of exercises you can do instead.
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts
So, now that you know a little more about partial and full deadlifts, let’s judge these exercises by a few different criteria:
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Strength
Partial and full deadlifts are both excellent strength-building exercises. They are ideal for low rep, heavy weight training, which is critical for building strength. However, because the movement/range of motion differs between these two exercises, so does the type of strength they develop.
Full deadlifts will develop full-range strength, particularly in your hamstrings and hips. They’re much more lower-body dominant. In contrast, partial deadlifts use a smaller range of motion and less lower-body engagement. They tend to emphasize the upper body more.
Therefore, you should choose the exercise that strengthens the muscles you want to develop – full deadlifts for the lower body and partials for your upper body.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: It’s a draw!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Hypertrophy
Both partial and full deadlifts are potent muscle builders. However, like building strength, each exercise tends to affect different parts of your body. Full deadlifts work your upper body and lower body reasonably equally, but partial deadlifts are more upper-body dominant.
Because of this, you must choose the right deadlift for the muscle groups you want to enlarge.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: It’s a draw!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Safety
While deadlifts can be performed safely, the loads and movements mean there is always a risk of injury, especially to the lower back. Biceps tears are also a problem during deadlifts, especially when using an alternating or mixed grip.
The reduced range of motion and more back-friendly starting position means that partial deadlifts are potentially safer than conventional deadlifts, especially for taller lifters and anyone with tight hamstrings.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: Partial deadlifts!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Ease of learning
The large range of motion and potentially awkward starting position means that full deadlifts can be hard for beginners. In contrast, the partial deadlift is harder to get wrong, as the bar is set at a more comfortable and reachable height.
However, most beginners should be able to learn either type of deadlift with proper instructions. In fact, the deadlift is a critical movement for all exercisers as it teaches you how to safely lift heavy objects off the floor, e.g., when picking dumbbells up off the floor to do curls.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: Partial deadlift, albeit only just!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Equipment
Full deadlifts are a very low-tech exercise. All you need is somewhere flat to stand, a barbell, and enough weight plates. You can do full deadlifts in a fancy gym, your garage, or even in your backyard.
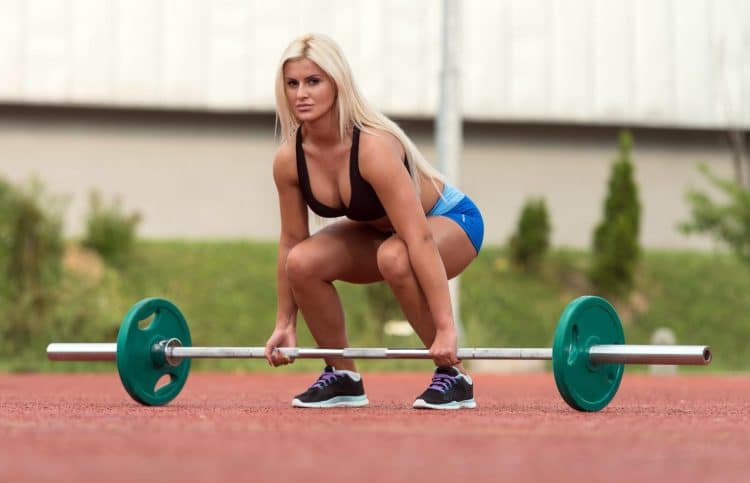

In contrast, you’ll need something to rest the bar on for partial deadlifts, be that a power rack or pulling blocks. Because of this, you may not have the equipment you need to do partial deadlifts.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: Full deadlifts!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Long-term progression
With partial deadlifts, your primary source of long-term progression is adding weight to the bar. You CAN reduce the height of your barbell, which will make the lift more challenging. Still, unless you lower the bar a fraction of an inch at a time, this is not a viable option for long-term progression.
In contrast, while you can add weight the same way with full deadlifts, there are also many variations you can use to maintain your progress, such as deficit and snatch grip deadlifts.
Many of these variations are designed to boost your conventional deadlift performance. However, they probably won’t do much to improve your partial deadlift.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: Full deadlift!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts vs. Full Deadlifts: Variety
As discussed above, partial deadlifts are already a variation of full deadlifts, and there are many more for you to try. Lifters do not tend to just do partial deadlifts and use other variations to keep their workouts fresh and productive.
In fact, powerlifters usually use partial deadlifts as an assistance or accessory exercise to improve their conventional deadlift lockout. Only strongmen compete in the partial deadlift.
[sc name=”style-summary-2nd” ]
Winner: Full deadlift!
[/sc]
Partial Deadlifts Vs. Full Deadlifts – Wrapping Up
Back in Victorian times, the deadlift was known as the health lift. It was considered one of the best exercises you could do for strength, endurance, fitness, and well-being. Nowadays, you are more likely to see exercisers doing leg presses than deadlifting, and the squat is arguably more popular than the deadlift.
However, in terms of bang for your buck, deadlifts are hard to beat. Very few exercises work as many muscles or are as functional as the deadlift. Sadly, though, because of prolonged sitting, many people are unsuited to deadlifts, and some gyms have even banned them.
So, are partial deadlifts better than full deadlifts, or is it the other way around? The truth is that both of these exercises are excellent, and either one would make a great addition to your lower body or back workouts.
Do full deadlifts for more of a full-body workout or partial deadlifts to emphasize your upper body.
Ultimately, any deadlift is a good deadlift, providing you perform it correctly, of course!
Read also: Romanian Deadlift Vs. Deadlift: Which One Should You Do?


